Amazon ECS and EKS
Please use the menu below to navigate the article sections:
- Amazon ECS vs Amazon EKS
- Launch Types
- ECS Terminology
- Images
- Tasks and Task Definitions
- ECS Clusters
- Service Scheduler
- Custom Scheduler
- ECS Container Agent
- Auto Scaling
- Security/SLA
- ECS with X-Ray
- ECS with Elastic Beanstalk
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
- Using an Amazon Elastic Load Balancer with ECS
- Amazon EKS

The Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) is a highly scalable, high performance container management service that supports Docker containers.
Amazon ECS allows you to easily run applications on a managed cluster of Amazon EC2 instances.
Amazon ECS eliminates the need for you to install, operate, and scale your own cluster management infrastructure.
Using API calls you can launch and stop container-enabled applications, query the complete state of clusters, and access features like security groups, Elastic Load Balancing, EBS volumes and IAM roles.
Amazon ECS can be used to schedule the placement of containers across clusters based on resource needs and availability requirements.
There is no additional charge for Amazon ECS. You pay for:
- Resources created with the EC2 Launch Type (e.g. EC2 instances and EBS volumes).
- The number and configuration of tasks you run for the Fargate Launch Type.
It is possible to use Elastic Beanstalk to handle the provisioning of an Amazon ECS cluster, load balancing, auto-scaling, monitoring, and placing your containers across your cluster.
Alternatively use ECS directly for more fine-grained control for customer application architectures.
It is possible to associate a service on Amazon ECS to an Application Load Balancer (ALB) for the Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) service.
The ALB supports a target group that contains a set of instance ports. You can specify a dynamic port in the ECS task definition which gives the container an unused port when it is scheduled on the EC2 instance.
You can use any AMI that meets the Amazon ECS AMI specification. For example, please follow the link regarding Amazon ECS-Optimized AMIs.
Amazon ECS vs Amazon EKS
Amazon also provide the Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes (Amazon EKS) which can be used to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications using Kubernetes on AWS.
The table below describes some of the differences between these services to help you understand when you might choose one over the other:
| Amazon ECS | Amazon EKS |
| Managed, highly available, highly scalable container platform | Managed, highly available, highly scalable container platform |
| AWS-specific platform that supports Docker Containers | Compatible with upstream Kubernetes so it’s easy to lift and shift from other Kubernetes deployments |
| Considered simpler and easier to use | Considered more feature-rich and complex with a steep learning curve |
| Leverages AWS services like Route 53, ALB, and CloudWatch | A hosted Kubernetes platform that handles many things internally |
| “Tasks” are instances of containers that are run on underlying compute but more of less isolated | “Pods” are containers collocated with one another and can have shared access to each other |
| Limited extensibility | Extensible via a wide variety of third-party and community add-ons. |
Launch Types
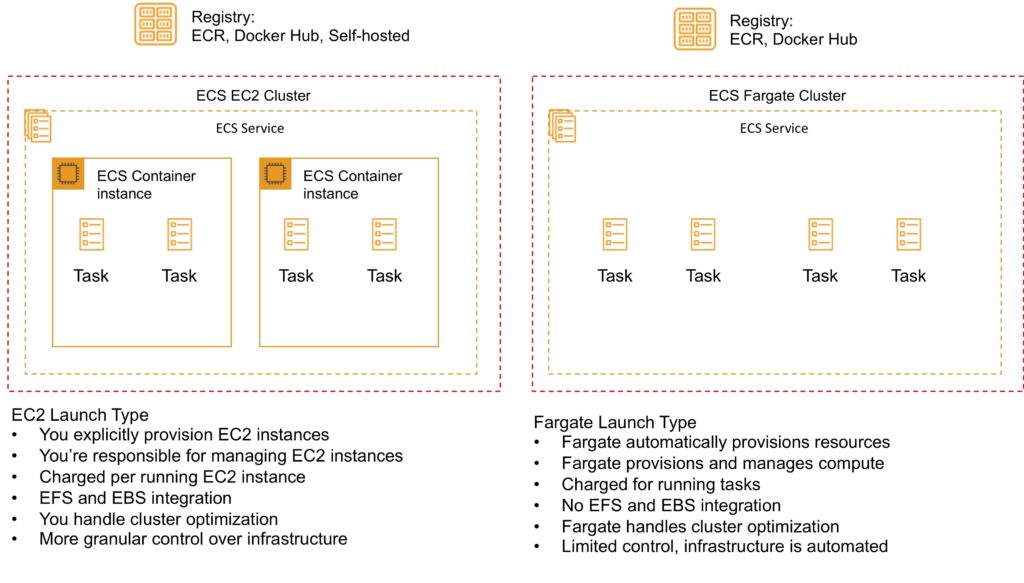
An Amazon ECS launch type determines the type of infrastructure on which your tasks and services are hosted.
There are two launch types, and the table below describes some of the differences between the two launch types:
| Amazon EC2 | Amazon Fargate |
| You can explicitly provision EC2 instances | The control plan asks for resources and Fargate automatically provisions |
| You’re responsible for upgrading, patching, care of EC2 pool | Fargate provisions compute as needed |
| You must handle cluster optimization | Fargate handles customer optimizations |
| More granular control over infrastructure | Limited control, as infrastructure is automated |
Fargate Launch Type
- The Fargate launch type allows you to run your containerized applications without the need to provision and manage the backend infrastructure. Just register your task definition and Fargate launches the container for you.
- Fargate Launch Type is a serverless infrastructure managed by AWS.
- Fargate only supports container images hosted on Elastic Container Registry (ECR) or Docker Hub.
EC2 Launch Type
- The EC2 launch type allows you to run your containerized applications on a cluster of Amazon EC2 instances that you manage.
- Private repositories are only supported by the EC2 Launch Type.
The following diagram shows the two launch types and summarizes some key differences:
ECS Terminology
The following table provides an overview of some of the terminology used with Amazon ECS:
| Amazon ECS Term | Definition |
| Cluster | Logical Grouping of EC2 Instances |
| Container Instance | EC2 instance running the ECS agent |
| Task Definition | Blueprint that describes how a docker container should launch |
| Task | A running container using settings in a Task Definition |
| Service | Defines long running tasks – can control task count with Auto Scaling and attach an ELB |
Images
Containers are created from a read-only template called an image which has the instructions for creating a Docker container.
Images are built from a Dockerfile.
Only Docker containers are currently supported.
An image contains the instructions for creating a Docker container.
Images are stored in a registry such as DockerHub or AWS Elastic Container Registry (ECR).
ECR is a managed AWS Docker registry service that is secure, scalable, and reliable.
ECR supports private Docker repositories with resource-based permissions using AWS IAM to access repositories and images.
Developers can use the Docker CLI to push, pull and manage images.
Tasks and Task Definitions
A task definition is required to run Docker containers in Amazon ECS.
A task definition is a text file in JSON format that describes one or more containers, up to a maximum of 10.
Task definitions use Docker images to launch containers.
You specify the number of tasks to run (i.e. the number of containers).
Some of the parameters you can specify in a task definition include:
- Which Docker images to use with the containers in your task.
- How much CPU and memory to use with each container.
- Whether containers are linked together in a task.
- The Docker networking mode to use for the containers in your task.
- What (if any) ports from the container are mapped to the host container instances.
- Whether the task should continue if the container finished or fails.
- The commands the container should run when it is started.
- Environment variables that should be passed to the container when it starts.
- Data volumes that should be used with the containers in the task.
- IAM role the task should use for permissions.
You can use Amazon ECS Run task to run one or more tasks once.
ECS Clusters
ECS Clusters are a logical grouping of container instances that you can place tasks on.
A default cluster is created but you can then create multiple clusters to separate resources.
ECS allows the definition of a specified number (desired count) of tasks to run in the cluster.
Clusters can contain tasks using the Fargate and EC2 launch type.
For clusters with the EC2 launch type clusters can contain different container instance types.
Each container instance may only be part of one cluster at a time.
“Services” provide auto-scaling functions for ECS.
Clusters are region specific.
You can create IAM policies for your clusters to allow or restrict users’ access to specific clusters.
Service Scheduler
You can schedule ECS using Service Scheduler and Custom Scheduler.
Ensures that the specified number of tasks are constantly running and reschedules tasks when a task fails.
Can ensure tasks are registered against an ELB.
Custom Scheduler
You can create your own schedulers to meet business needs.
Leverage third party schedulers such as Blox.
The Amazon ECS schedulers leverage the same cluster state information provided by the Amazon ECS API to make appropriate placement decisions.
ECS Container Agent
The ECS container agent allows container instances to connect to the cluster.
The container agent runs on each infrastructure resource on an ECS cluster.
The ECS container agent is included in the Amazon ECS optimized AMI and can also be installed on any EC2 instance that supports the ECS specification (only supported on EC2 instances).
Linux and Windows based.
For non-AWS Linux instances to be used on AWS you must manually install the ECS container agent.
Auto Scaling
Service Auto Scaling
Amazon ECS service can optionally be configured to use Service Auto Scaling to adjust the desired task count up or down automatically.
Service Auto Scaling leverages the Application Auto Scaling service to provide this functionality.
Amazon ECS Service Auto Scaling supports the following types of scaling policies:
- Target Tracking Scaling Policies—Increase or decrease the number of tasks that your service runs based on a target value for a specific CloudWatch metric. This is similar to the way that your thermostat maintains the temperature of your home. You select temperature and the thermostat does the rest.
- Step Scaling Policies—Increase or decrease the number of tasks that your service runs in response to CloudWatch alarms. Step scaling is based on a set of scaling adjustments, known as step adjustments, which vary based on the size of the alarm breach.
- Scheduled Scaling—Increase or decrease the number of tasks that your service runs based on the date and time.
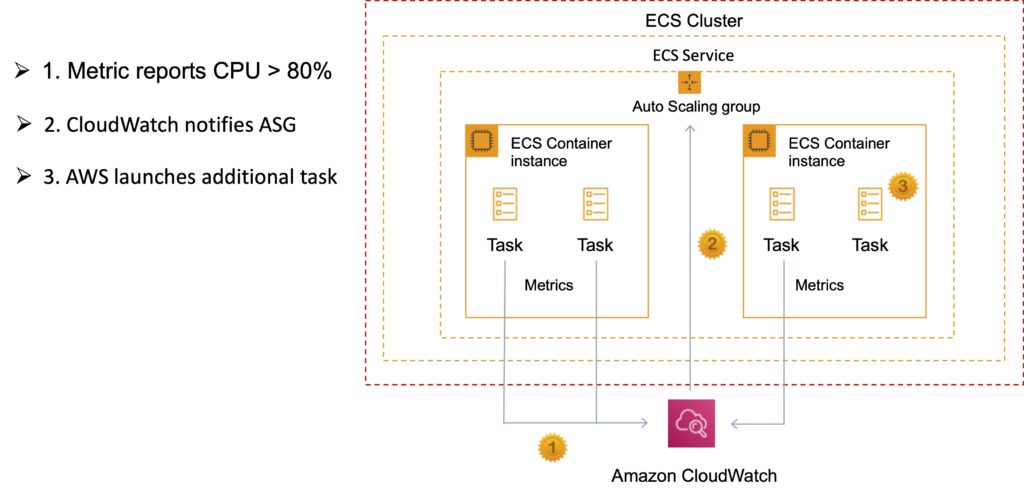
Cluster Auto Scaling
Uses an Amazon ECS resource type called a Capacity Provider.
A Capacity Provider can be associated with an EC2 Auto Scaling Group (ASG).
When you associate an ECS Capacity Provider with an ASG and add the Capacity Provider to an ECS cluster, the cluster can now scale your ASG automatically by using two new features of ECS:
- Managed scaling, with an automatically created scaling policy on your ASG, and a new scaling metric (Capacity Provider Reservation) that the scaling policy uses; and
- Managed instance termination protection, which enables container-aware termination of instances in the ASG when scale-in happens.

Security/SLA
EC2 instances use an IAM role to access ECS.
IAM can be used to control access at the container level using IAM roles.
The container agent makes calls to the ECS API on your behalf through the applied IAM roles and policies.
You need to apply IAM roles to container instances before they are launched (EC2 launch type).
Assign extra permissions to tasks through separate IAM roles (IAM Roles for Tasks).
ECS tasks use an IAM role to access services and resources.
Security groups attach at the instance or container level.
You have root level access to the operating system of the EC2 instances.
The Compute SLA guarantees a Monthly Uptime Percentage of at least 99.99% for Amazon ECS.
ECS with X-Ray
There are two ways to run X-Ray:
As a daemon: X-Ray agent runs in a daemon container.
As a “sidecar”: X-Ray runs alongside each container.
For Fargate the X-Ray daemon only runs as a sidecar.
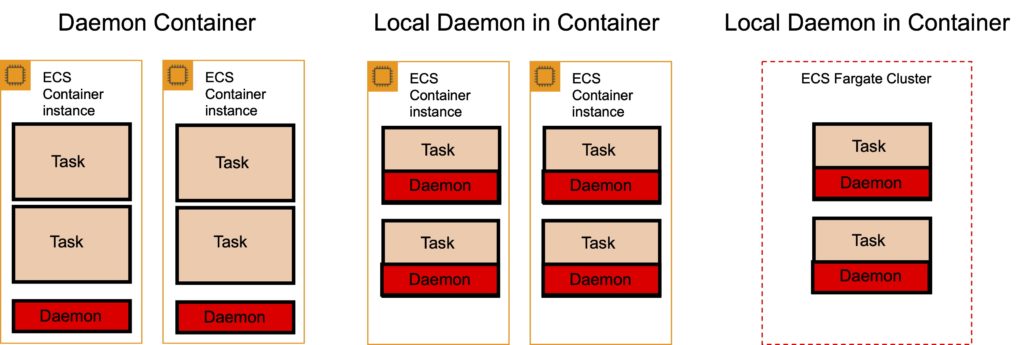
Task definition:
- X-Ray runs on port 2000 UDP.
- Must specify the daemon address.
- Must link the containers together.
X-Ray provides a Docker container image that you can deploy alongside your application:
- Command: docker pull amazon/aws-xray-daemon
ECS with Elastic Beanstalk
There are two options: Single and Multi- Docker container mode.
Single Container Docker
The single container platform can be used to deploy a Docker image (described in a Dockerfile or Dockerrun.aws.json definition) and source code to EC2 instances running in an Elastic Beanstalk environment.
Use the single container platform when you only need to run one container per instance.
Multicontainer Docker
The other basic platform, Multicontainer Docker, uses the Amazon Elastic Container Service to coordinate the deployment of multiple Docker containers to an Amazon ECS cluster in an Elastic Beanstalk environment.
The instances in the environment each run the same set of containers, which are defined in a Dockerrun.aws.json file.
Use the multicontainer platform when you need to deploy multiple Docker containers to each instance.
ElasticBeanstalk creates the following resources:
- ECS cluster.
- EC2 container instances.
- Load balancers (for high availability mode).
- Task definitions and execution.
Requires a config file Dockerrun.aws.json at the root of the source code.
Your Docker images must be pre-built (can be stored in ECR).
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) is a fully managed Docker container registry that makes it easy for developers to store, manage, and deploy Docker container images.
Amazon ECR is integrated with Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS).
Amazon ECR hosts your images in a highly available and scalable architecture, allowing you to reliably deploy containers for your applications.
Integration with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) provides resource-level control of each repository.
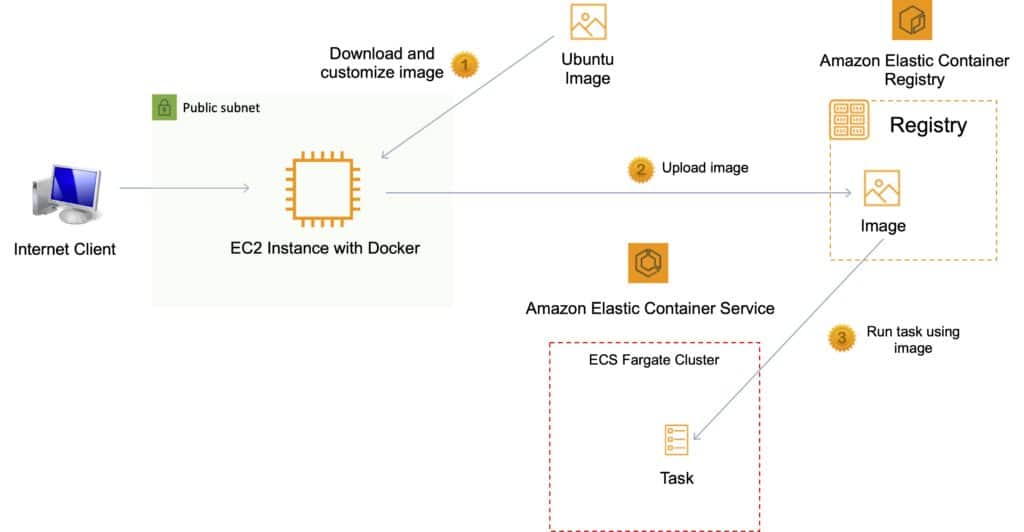
Pushing and Pulling Images to ECR
You must first authenticate.
To authenticate Docker to an Amazon ECR registry with get-login-password, run the aws ecr get-login-password command:
- aws ecr get-login-password –region us-east-1 | docker login –username AWS –password-stdin aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
Tag your image:
- docker tag e9ae3c220b23 aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.region.amazonaws.com/my-web-app
Push the image using the docker push command:
- docker push aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.region.amazonaws.com/my-web-app
Pull the image using the docker pull command. The image name format should be registry/repository[:tag] to pull by tag, or registry/repository[@digest] to pull by digest.
- docker pull aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.region.amazonaws.com/my-web-app:e9ae3c220b23
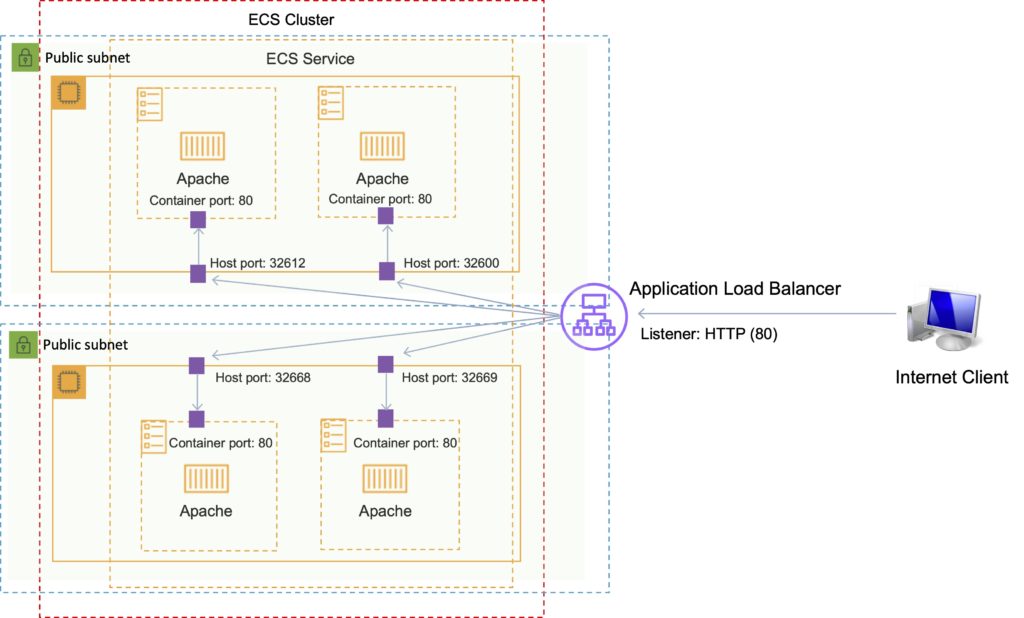
Using an Amazon Elastic Load Balancer with ECS
It is possible to associate a service on Amazon ECS to an Amazon Elastic Load Balancer (ELB).
The ALB supports a target group that contains a set of instance ports.
You can specify a dynamic port in the ECS task definition which gives the container an unused port when it is scheduled on the EC2 instance (this is specific to ALB only).
Amazon EKS
The Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) is a managed service for running Kubernetes on AWS and on-premises.
Amazon EKS can run on Amazon EC2 or AWS Fargate.
Integrates with Application Load Balancers, AWS IAM for RBA and Amazon VPC.
Amazon EKS provides a scalable and highly available Kubernetes control plane running across multiple AWS Availability Zones (AZs).
Amazon EKS automatically manages availability and scalability of Kubernetes API servers and etcd persistence layer.
Amazon EKS runs the Kubernetes control plane across three AZs to ensure high availability, and automatically detects and replaces unhealthy control plane nodes.
Exam tip: The principle use case is when organizations need a consistent control plane for managing containers across hybrid clouds and multicloud environments.




