Amazon OpenSearch
Please use the menu below to navigate the article sections:

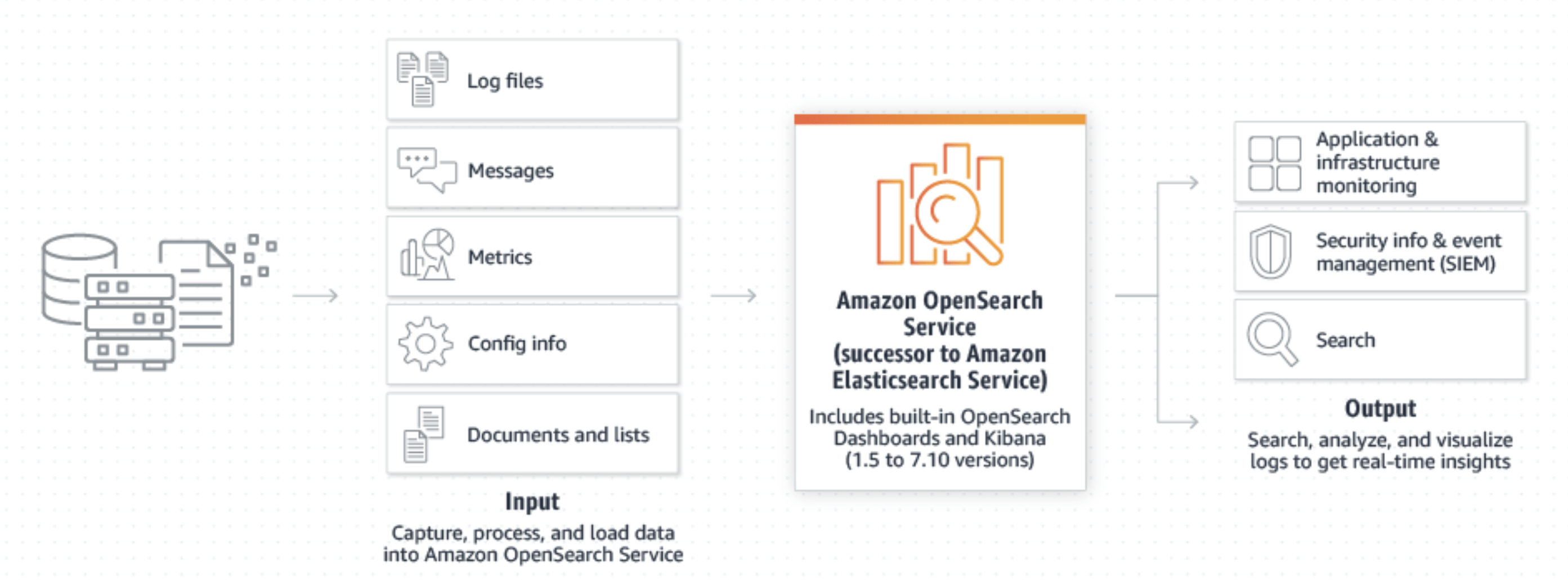
The Amazon OpenSearch Service is the successor to the Amazon Elasticsearch Service.
Amazon OpenSearch Service is an open source, distributed search and analytics suite based on Elasticsearch.
Elasticsearch is a distributed search and analytics engine built on Apache Lucene.
Elasticsearch is a popular search engine commonly used for log analytics, full-text search, security intelligence, business analytics, and operational intelligence use cases.
With OpenSearch you can perform log analytics interactively, perform real-time application monitoring, website search, performance metric analysis and more.
You can choose from a variety of open-source engine options for your OpenSearch cluster.
Options include the latest version of OpenSearch and many versions of ALv2 Elasticsearch.
Deployment and Monitoring
An OpenSearch cluster can be created using the AWS Management Console, API, or AWS CLI.
Specify the number of instances, instance types, and storage options.
In-place upgrades can be performed without downtime.
Provides built-in monitoring and alerting with automatic notifications.
You can configure alerts using the Kibana or OpenSearch Dashboards and the REST API.
Notifications can be sent via custom webhooks, Slack, Amazon SNS, and Amazon Chime.
OpenSearch Service supports multiple query languages such as:
- Domain-Specific Language (DSL).
- SQL queries with OpenSearch SQL.
- OpenSearch Piped Processing Language (PPL).
OpenSearch integrates with open-source tools including:
- Logstash.
- OpenTelemetry.
- ElasticSearch APIs.
OpenSearch in an Amazon VPC
OpenSearch Services domains can be launched into an Amazon VPC.
Using a VPC enables secure communication between the OpenSearch Service and other services within the VPC.
The following are some of the ways VPC domains differ from public domains.
- Because of their logical isolation, domains that reside within a VPC have an extra layer of security compared to domains that use public endpoints.
- While public domains are accessible from any internet-connected device, VPC domains require some form of VPN or proxy.
- Compared to public domains, VPC domains display less information in the console. Specifically, the Cluster health tab does not include shard information, and the Indices tab isn’t present.
- The domain endpoints take different forms (https://search-domain-name vs. https://vpc-domain-name).
- You can’t apply IP-based access policies to domains that reside within a VPC because security groups already enforce IP-based access policies.
Note the following limitations:
- If you launch a new domain within a VPC, you can’t later switch it to use a public endpoint. The reverse is also true.
- You can either launch your domain within a VPC or use a public endpoint, but you can’t do both.
- You can’t launch your domain within a VPC that uses dedicated tenancy. You must use a VPC with tenancy set to Default.
- After you place a domain within a VPC, you can’t move it to a different VPC, but you can change the subnets and security group settings.
- To access the default installation of OpenSearch Dashboards for a domain that resides within a VPC, users must have access to the VPC.
The ELK Stack
ELK is an acronym that describes a popular combination of projects: Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana.
The ELK stack gives you the ability to aggregate logs from all your systems and applications, analyze these logs, and create visualizations.
ELK is useful for visualizing application and infrastructure monitoring data, troubleshooting, security analytics and more.
Security
OpenSearch Service domains offer encryption of data at rest.
Uses AWS KMS for storage and management of encryption keys.
Encryption uses AES-256.
Encryption also encrypts node-to-node communications using TLS 1.2.
Node-to-node encryption is optional and can be enabled through the console, CLI, or API.
Once node-to-node encryption is enabled it cannot be disabled. Instead you must create a new domain from a snapshot without this setting enabled.
Amazon OpenSearch Service supports three types of access policies:
Fine-grained access control offers additional capabilities within Amazon OpenSearch Service.
Fine-grained access control offers the following benefits:
- Role-based access control.
- Security at the index, document, and field level.
- OpenSearch Dashboards multi-tenancy.
- HTTP basic authentication for OpenSearch and OpenSearch Dashboards.
OpenSearch Service supports authentication through SAML and Amazon Cognito.




