Amazon Aurora
Please use the menu below to navigate the article sections:

Amazon Aurora is a relational database service that combines the speed and availability of high-end commercial databases with the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of open-source databases.
Aurora is an AWS proprietary database.
Fully managed service.
High performance, low price.
2 copies of data are kept in each AZ with a minimum of 3 AZ’s (6 copies).
Can handle the loss of up to two copies of data without affecting DB write availability and up to three copies without affecting read availability.
The following diagram depicts how Aurora Fault Tolerance and Replicas work:
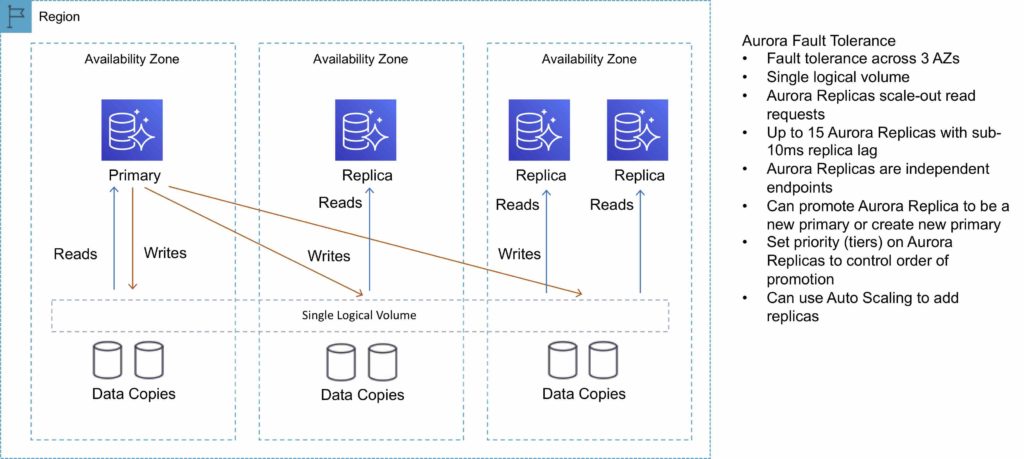
Aurora Replicas
There are two types of replication: Aurora replica (up to 15), MySQL Read Replica (up to 5).
The table below describes the differences between the two replica options:
| Feature | Aurora Replica | MySQL Replica |
| Number of replicas | Up to 15 | Up to 5 |
| Replication type | Asynchronous (milliseconds) | Asynchronous (seconds) |
| Performance impact on primary | Low | High |
| Replica location | In-region | Cross-region |
| Act as failover target | Yes (no data loss) | Yes (potentially minutes of data loss) |
| Automated failover | Yes | No |
| Support for user-defined replication delay | No | Yes |
| Support for different data or schema vs. primary | No | Yes |
You can create read replicas for an Amazon Aurora database in up to five AWS regions. This capability is available for Amazon Aurora with MySQL compatibility.
Cross-Region Read Replicas
Cross-region read replicas allow you to improve your disaster recovery posture, scale read operations in regions closer to your application users, and easily migrate from one region to another.
Cross-region replicas provide fast local reads to your users.
Each region can have an additional 15 Aurora replicas to further scale local reads.
You can choose between Global Database, which provides the best replication performance, and traditional binlog-based replication.
You can also set up your own binlog replication with external MySQL databases.
The following diagram depicts the Cross-Region Read Replica topology:
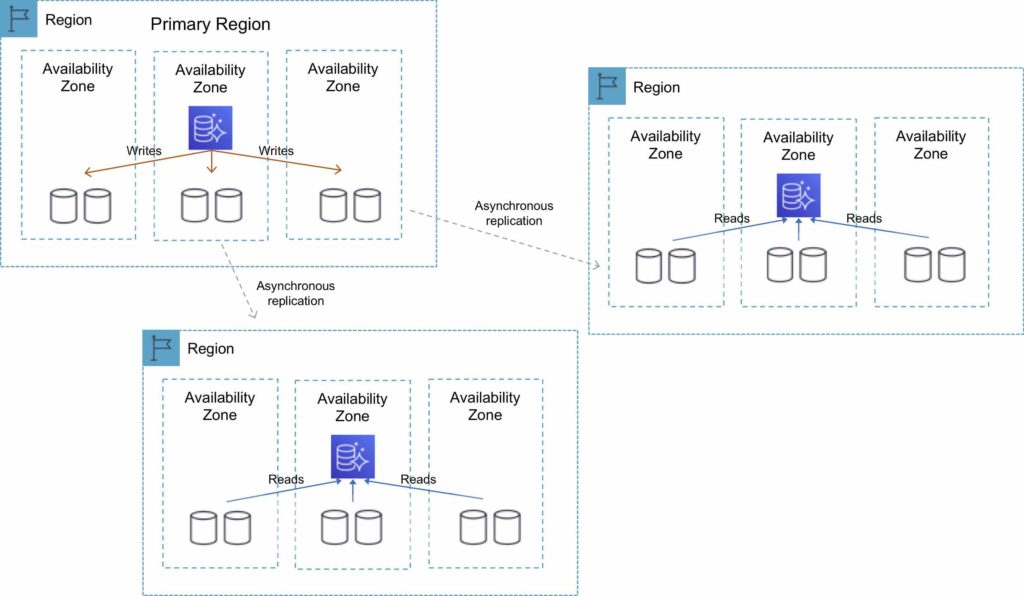
Global Database
For globally distributed applications you can use Global Database, where a single Aurora database can span multiple AWS regions to enable fast local reads and quick disaster recovery.
Global Database uses storage-based replication to replicate a database across multiple AWS Regions, with typical latency of less than 1 second.
You can use a secondary region as a backup option in case you need to recover quickly from a regional degradation or outage.
A database in a secondary region can be promoted to full read/write capabilities in less than 1 minute.
The following table depicts the Aurora Global Database topology:
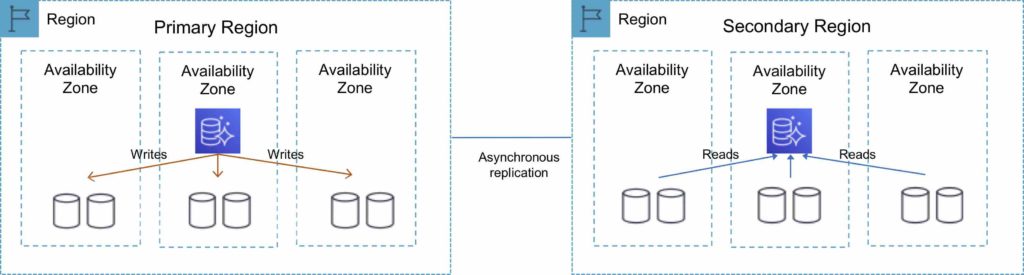
Multi-Master
Amazon Aurora Multi-Master is a new feature of the Aurora MySQL-compatible edition that adds the ability to scale out write performance across multiple Availability Zones, allowing applications to direct read/write workloads to multiple instances in a database cluster and operate with higher availability.
Aurora Multi-Master is designed to achieve high availability and ACID transactions across a cluster of database nodes with configurable read after write consistency.
Architecture
An Aurora cluster consists of a set of compute (database) nodes and a shared storage volume.
The storage volume consists of six storage nodes placed in three Availability Zones for high availability and durability of user data.
Every database node in the cluster is a writer node that can run read and write statements.
There is no single point of failure in the cluster.
Applications can use any writer node for their read/write and DDL needs.
A database change made by a writer node is written to six storage nodes in three Availability Zones, providing data durability and resiliency against storage node and Availability Zone failures.
The writer nodes are all functionally equal, and a failure of one writer node does not affect the availability of the other writer nodes in the cluster.
High Availability
Aurora Multi-Master improves upon the high availability of the single-master version of Amazon Aurora because all the nodes in the cluster are read/write nodes.
With single-master Aurora, a failure of the single writer node requires the promotion of a read replica to be the new writer.
In the case of Aurora Multi-Master, the failure of a writer node merely requires the application using the writer to open connections to another writer.
Aurora Serverless
Amazon Aurora Serverless is an on-demand, auto-scaling configuration for Amazon Aurora.
Available for MySQL-compatible and PostgreSQL-compatible editions.
The database automatically starts up, shuts down, and scales capacity up or down based on application needs.
It enables you to run a database in the cloud without managing any database instances. It’s a simple, cost-effective option for infrequent, intermittent, or unpredictable workloads.
You simply create a database endpoint and optionally specify the desired database capacity range and connect applications.
With Aurora Serverless, you only pay for database storage and the database capacity and I/O your database consumes while it is active.
Pay on a per-second basis for the database capacity you use when the database is active.
Can migrate between standard and serverless configurations with a few clicks in the Amazon RDS Management Console.
The table below provides a few example use cases for Amazon Aurora Serverless:
| Use Case | Example |
| Infrequently Used Applications | Application that is only used for a few minutes several times per day or week. Need a cost-effective database that only requires you to pay when it’s active. With Aurora Serverless, you only pay for the database resources you consume. |
| New Applications | Deploying a new application and are unsure which instance size you need. With Aurora Serverless, you simply create an endpoint and let the database auto-scale to the capacity requirements of your application. |
| Variable Workloads | Running a lightly used application, with peaks of 30 minutes to several hours a few times each day or several times per year. Now you only pay for what the resources needed based on load – avoiding paying for unused resources or risking poor performance. |
| Unpredictable Workloads | Running workloads where there is database usage throughout the day, and peaks of activity that are hard to predict. With Aurora Serverless, your database will auto-scale capacity to meet the needs of the application’s peak load and scale back down when the surge of activity is over. |
| Development and Test Databases | Software development and QA teams are using databases during work hours, but don’t need them on nights or weekends. With Aurora Serverless, your database automatically shuts down when not in use, and starts up much more quickly when work starts the next day. |
| Multitenant Applications | Web-based application with a database for each of your customers. Now you don’t have to manage database capacity individually for each application in your fleet. Aurora manages individual database capacity for you, saving you valuable time. |
Fault-Tolerant and Self-Healing Storage
Each 10GB chunk of your database volume is replicated six ways, across three Availability Zones.
Amazon Aurora storage is fault-tolerant, transparently handling the loss of up to two copies of data without affecting database write availability and up to three copies without affecting read availability.
Amazon Aurora storage is also self-healing; data blocks and disks are continuously scanned for errors and replaced automatically.
Aurora Auto Scaling
Aurora Auto Scaling dynamically adjusts the number of Aurora Replicas provisioned for an Aurora DB cluster using single-master replication.
Aurora Auto Scaling is available for both Aurora MySQL and Aurora PostgreSQL.
Aurora Auto Scaling enables your Aurora DB cluster to handle sudden increases in connectivity or workload.
When the connectivity or workload decreases, Aurora Auto Scaling removes unnecessary Aurora Replicas so that you don’t pay for unused provisioned DB instances.
Backup and Restore
Amazon Aurora’s backup capability enables point-in-time recovery for your instance.
This allows you to restore your database to any second during your retention period, up to the last five minutes.
Your automatic backup retention period can be configured up to thirty-five days.
Automated backups are stored in Amazon S3, which is designed for 99.999999999% durability. Amazon Aurora backups are automatic, incremental, and continuous and have no impact on database performance.
When automated backups are turned on for your DB Instance, Amazon RDS automatically performs a full daily snapshot of your data (during your preferred backup window) and captures transaction logs (as updates to your DB Instance are made).
Automated backups are enabled by default and data is stored on S3 and is equal to the size of the DB.
Amazon RDS retains backups of a DB Instance for a limited, user-specified period called the retention period, which by default is 7 days but can be up to 35 days.
There are two methods to backup and restore RDS DB instances:
- Amazon RDS automated backups.
- User initiated manual backups.
Both options back up the entire DB instance and not just the individual DBs.
Both options create a storage volume snapshot of the entire DB instance.
You can make copies of automated backups and manual snapshots.
Automated backups backup data to multiple AZs to provide for data durability.
Multi-AZ backups are taken from the standby instance (for MariaDB, MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL).
The DB instance must be in an Active state for automated backups to happen.
Only automated backups can be used for point-in-time DB instance recovery.
The granularity of point-in-time recovery is 5 minutes.
Amazon RDS creates a daily full storage volume snapshot and captures transaction logs regularly.
You can choose the backup window.
There is no additional charge for backups, but you will pay for storage costs on S3.
You can disable automated backups by setting the retention period to zero (0).
An outage occurs if you change the backup retention period from zero to a non-zero value or the other way around.
The retention period is the period AWS keeps the automated backups before deleting them.
Retention periods:
- By default the retention period is 7 days if configured from the console for all DB engines except Aurora.
- The default retention period is 1 day if configured from the API or CLI.
- The retention period for Aurora is 1 day regardless of how it is configured.
- You can increase the retention period up to 35 days.
During the backup window I/O may be suspended.
Automated backups are deleted when you delete the RDS DB instance.
Automated backups are only supported for InnoDB storage engine for MySQL (not for myISAM).
When you restore a DB instance the default DB parameters and security groups are applied – you must then apply the custom DB parameters and security groups.
You cannot restore from a DB snapshot into an existing DB instance.
Following a restore the new DB instance will have a new endpoint.
The storage type can be changed when restoring a snapshot.




